Non-mineral powder types and application differences
Inorganic non-metallic mineral powder filler, referred to as non-mineral powder, is widely used in plastics, rubber, coatings, paper, wire and cable, electronic packaging and other products, mainly filler to reduce the role of the cost of production costs at the same time, to improve the product performance, improve the processing of the material, so as to enhance the competitiveness of enterprises. The common non-mineral powder fillers in the market are: calcium carbonate, talcum powder, barium sulfate, silica micropowder, wollastonite powder, mica powder, kaolin, bentonite and so on. With the downstream enterprises on the physical properties of materials more and more demanding, non-mineral powder filler is also with the customer requirements, and gradually towards the direction of high purity, ultrafine, functionalization.
I. Classification of fillers
According to the chemical composition:
Divided into hydroxide, salt, monomers, complexes.
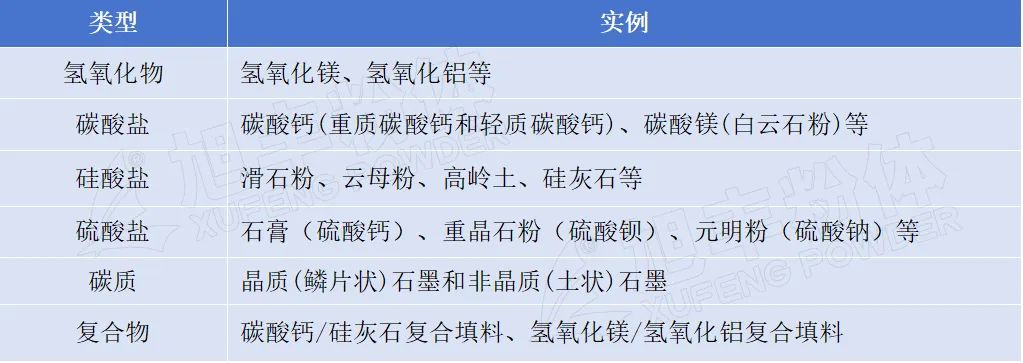
Table 1. Inorganic non-metallic mineral fillers classified according to chemical composition
According to the geometry:
Divided into spherical, cubic, block or short column, flake, fibrous
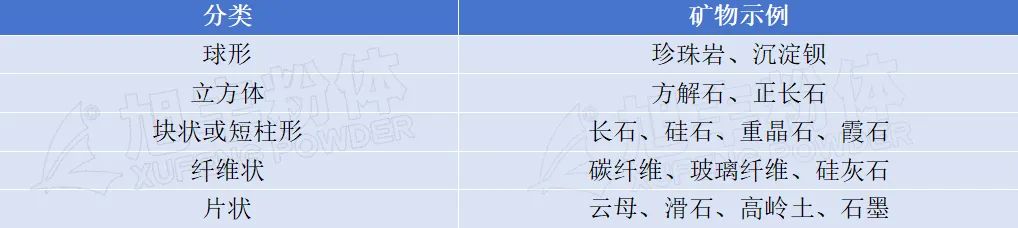
Table 2.Classification of non-metallic mineral fillers according to geometric shape
Second, the filler application differences
Calcium carbonate and talc are inorganic non-metallic mineral powder filler among the two common, because of the low price, abundant production has become the first choice of industrial filler, the next main introduction of calcium carbonate and talc applications and differences.
Application of calcium carbonate
Generally speaking, calcium carbonate is the non-mineral filler in the most abundant resources, the most inexpensive products. Therefore, it has almost become the first choice of non-mineral fillers, i.e., if calcium carbonate powder can meet the needs of filling and related functions, it will not consider other fillers which are more expensive.
Calcium carbonate is divided into heavy calcium and light calcium, heavy calcium carbonate processing is mainly through mechanical crushing, grinding methods; light calcium carbonate production is through the chemical reaction precipitation after the production of the latter than the former process is much more complex, the requirements are correspondingly stringent, so the same particle size of the light calcium carbonate to heavy calcium carbonate is more expensive than about 30%, if the performance allows you to choose the heavy calcium carbonate more cost-effective.

Application of talcum powder
Talc has excellent physical and chemical properties such as lubricity, acid and alkali resistance, insulation, high melting point, good covering power, good luster, strong adsorption. It has a wide range of applications in plastics, rubber, paper, paint and other industries.

The difference between calcium carbonate and talcum powder
Talc and calcium carbonate as fillers in different fields play different roles and have their own advantages, such as:
①Talcum powder is in the form of flakes, which has higher rigidity, dimensional stability and heat distortion temperature, and good strengthening effect;
② calcium carbonate is generally granular, stiffness and other aspects of performance is not as good as talcum powder, but the price is low, and high whiteness, plastic impact, toughness, small impact;
③ talc has a nucleating effect on polypropylene, and calcium carbonate in this regard, the effect is not obvious;
④ in the paint calcium carbonate and talc compared to calcium carbonate can reduce the rate of chalking, improve the light-colored paint color retention and increase the resistance to mold.




